How To Operate A Stamping Machine ?
In manufacturing operations, a stamping machine is an equipment that forms metal sheets or other materials into desired shapes or pieces. As the punch press, it is frequently utilized for the production of hardware stamping like, electronics, automotive parts, and aerospace parts. I will give a general overview of the operation of a standard stamping press in this explanation.
What's Is A Stamping Machine?
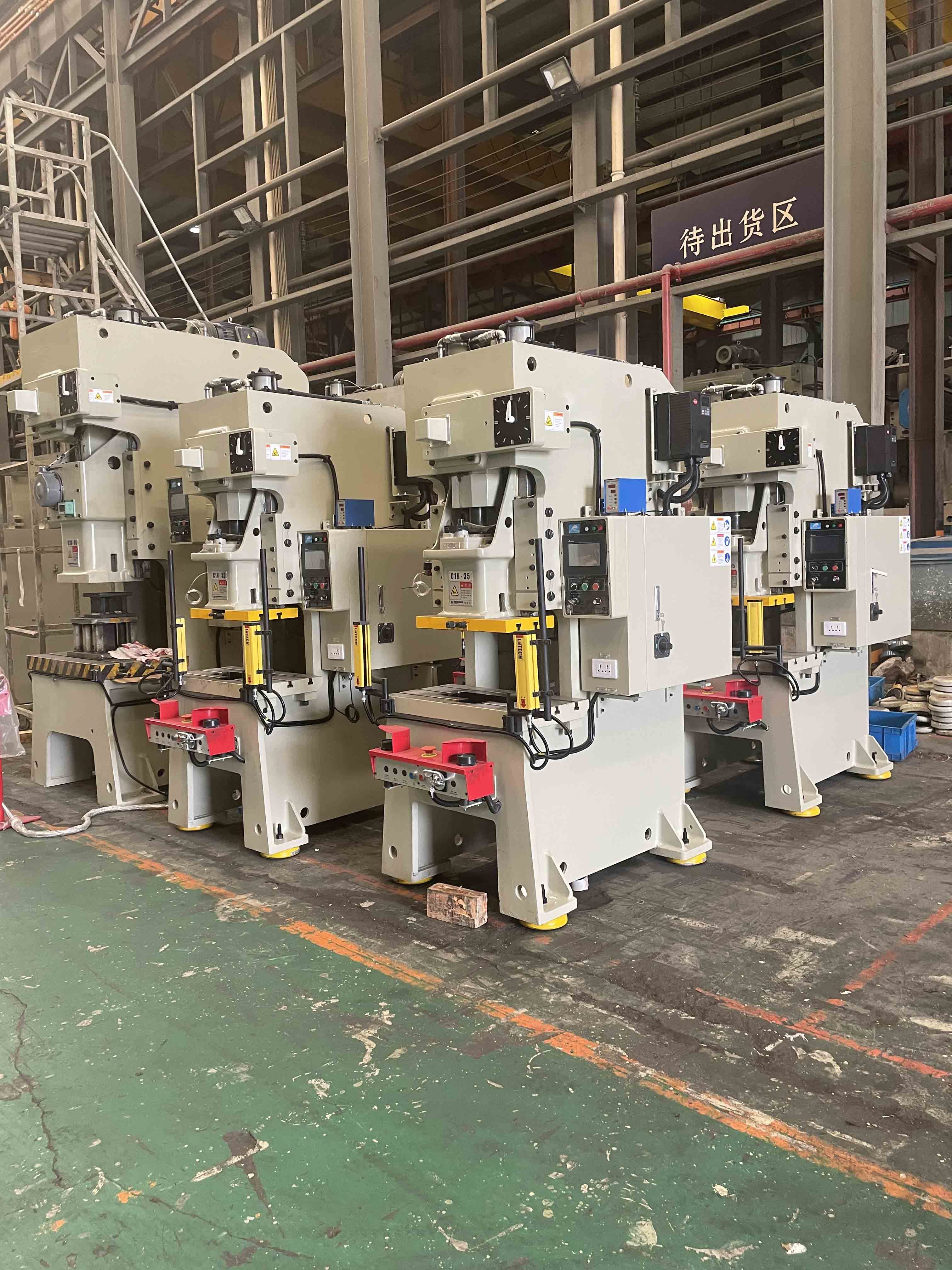

A stamping machine is a type of industrial equipment used to shape or cut materials, typically metal, through a process called stamping. It uses a die and a punch to apply pressure, transforming flat sheets of material into specific shapes or parts. Stamping machines can perform a variety of operations, such as cutting, bending, or embossing, and are commonly used in manufacturing sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics to efficiently produce components.
What Basic Component Does A Stamping Machine Has?
The following are some of the fundamental parts of a stamping machine:
Frame: The punch press is supported and given structure by the frame. Usually constructed of heavy-duty steel, it is intended to endure the stresses produced during the stamping operation.
Bed: The stamping press's bottom has a sizable, level surface that serves as the bed. It offers a solid foundation for the subject matter being worked on.
Ram: The punch press's moving part is called the ram. It moves up and down to exert force on the material and is attached to the upper portion of the frame.
Die Set: A customized tooling system made composed of upper and lower dies. The upper die is fastened to the ram, while the lower die is mounted on the bed. The dies contain voids or curves that define the final shape of the part.
How To Operate A Stamping Machine ?
A stamping machine operates in a succession of steps:
Material Preparation: The process begins with preparing the material, which is often a metal sheet or coil. To increase workability and reduce friction, the material may be cleaned, lubricated, or otherwise treated.
Feeding: The material is subsequently loaded into the stamping press. This can be done either manually or with an automatic feeding system. The material is moved between the upper and lower dies to ensure accurate alignment.
Die Closure: Once the material is in place, the ram advances downward, causing the top and lower dies to close together. This produces a hollow that corresponds to the desired shape of the final product.
Material Deformation: As the dies close, the material experiences considerable pressure and stress. This causes the material to deform and adopt the shape of the die cavity. The amount of force applied is determined by the material's characteristics and the intricacy of the part being produced.
Ejection: It occurs when the dies open and the ram returns to its original position. At this point, an ejection system may be used to extract the part from the dies. This may include the employment of ejector pins, air jets, or other techniques.
How To Choose A Right Stamping Machine For Your Project ?
Choosing the right stamping machine for your project involves several key considerations:
1, Project Requirements:
Determine the type of parts you need to produce. Consider the material, thickness, and complexity of the designs.
2, Machine Type:
Select between mechanical, hydraulic, or servo-driven stamping machines based on your project needs. Mechanical machines are typically faster, while hydraulic machines offer more flexibility.
3, Tonage Capacity:
Ensure the machine has sufficient tonnage to handle the material thickness and type. Calculate the required tonnage based on the material's yield strength and the size of the part.
4, Speed and Production Volume:
Consider the machine's cycle time and whether it meets your production volume requirements. Higher speeds are necessary for large-scale production.
5, Precision and Tolerance:
Evaluate the machine's ability to produce parts with the required precision and tolerances. This is crucial for industries with strict quality standards.
6, Ease of Setup and Changeover:
Look for machines that allow quick setup and easy changeover for different part designs, which can reduce downtime.
7, Maintenance and Support:
Consider the availability of technical support, spare parts, and maintenance services. Machines with reliable service options can save time and costs in the long run.
8, Budget:
Factor in the initial purchase cost as well as operating and maintenance costs. Ensure it aligns with your budget while meeting your production needs.
9, Manufacturer Reputation:
Research the manufacturer’s reputation and customer reviews. Choose a company known for quality and reliability in stamping machinery.
10, Safety Features:
Check for safety features and compliance with industry standards to protect operators and maintain a safe working environment.
By carefully assessing these factors, you can choose a stamping machine that best fits your project requirements and production goals.
What Stamping Machines Does Fanty Machinery Produce ?
A specialized mechanical device used in metal stamping processes to rapidly form and shape metal sheets. It operates at exceptionally high stroke rates, enabling the production of a large volume of parts in a short amount of time.
A precision tool commonly used in metalworking industries to create accurate holes, notches, and shapes in metal components. It employs carefully crafted dies and tools to achieve consistent results with minimal material waste.
A heavy-duty press system that excels in high-precision metal punching and forming tasks. It features a robust H-frame structure that ensures stability and accuracy during operations.
How To Contact Fanty Machinery ?
If you are looking for a quotation or custom your press line project, one of our Sales Engineers to help you with your project becomes the only decision to make. Contact us fanty@sz-fanty.com now !